What Is Psoriatic Arthritis & How Do You Treat It?
What is Psoriatic Arthritis
Arthritis describes any condition where cartilage in the joint breaks down. Normally, a joint consists of two smooth, cartilage-covered bone surfaces that fit together as a matched set and glide against one other. Arthritis can result when these smooth surfaces become irregular as the cartilage breaks down. This results in surfaces that don’t fit well together anymore, essentially “wearing out.
Psoriatic arthritis is a condition in which the lining of the joint gets inflamed and swollen. Because this inflammation stretches the tissues that keep the joint strong, the joint may become loose or crooked. Also, the smooth ends of the bones wear out, and the bone may lose its normal shape. Psoriatic arthritis can affect any joint in the body, and it affects men and women equally.
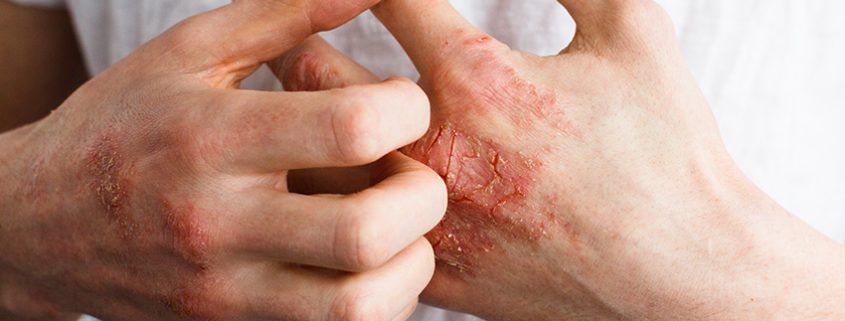
Psoriasis is a skin condition where people’s skin becomes dry, red, and flaky (Figure 1). It can affect any part of the body. Up to 30% of people with psoriasis develop psoriatic arthritis, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
Arthritis can be debilitating when it affects the hands and fingers. The most common forms of arthritis in the hand are osteoarthritis, post-traumatic arthritis (after an injury), and rheumatoid arthritis. Other causes of arthritis of the hand are infections, gout, and psoriasis.
The changes in the joints with psoriatic arthritis are a lot like those in rheumatoid arthritis. These symptoms can include:
- Red and swollen joints
- Joints that sometimes feel warm
- Decreased joint motion and stiff-feeling joints
With this condition, the hands may not be affected equally. It may be hard to tell psoriatic arthritis from other types of arthritis because most types of arthritis have symptoms of stiffness, swelling, and pain. In psoriatic arthritis, the swelling often affects the whole finger but more at the middle joint (figure 2). There may be pitting, ridging or crumbling of the fingernails. The joint at the end of the finger may become deformed (figure 3). Other parts of the hand and wrist are not usually affected.
Diagnosis
Psoriatic arthritis is suspected when people have psoriasis and develop problems with their joints. The doctor will mainly look at and feel the hand and look at x-rays. X-rays may show loss of the normal shape of the bone, mainly at the end joint. X-rays may also show swelling around the bone, and the space between the bones may become narrow. The bones may fuse together at a joint. There is no special blood test to find out if one has this arthritis. A piece of skin can be removed to help find out if a person has psoriasis.
Treatment
There is no cure for psoriatic arthritis, but there are medications available to help lessen swelling, redness, and pain to keep the hands functioning as well as possible. Different medical specialists usually work together to help with the treatment of this arthritis, including physicians and therapists.
Surgery may help treat the problems of psoriatic arthritis. The type of surgery needed depends on the problems one has with use and pain. A hand surgeon will help guide you to the best treatment for your particular concerns.
Orthopedic Sports Medicine Center of Oregon is located in Downtown Portland Oregon. Dr. Dominic Patillo, one of our Board-Certified Orthopedic Surgeons, specializes in hand surgery. His practice focuses on the treatment of both simple and complex hand and upper extremity conditions as well as general orthopaedic trauma. He is experienced with modern microsurgical techniques including nerve and vessel reconstruction.
Common problems treated include:
- carpal tunnel syndrome
- tennis elbow
- wrist pain
- sports injuries of the hand and wrist
- fractures of the hand, wrist, and forearm
- trigger finger
Other problems treated can include arthritis, nerve and tendon injuries, and congenital limb differences (birth defects).
If you have pain in your fingers, hand, wrist or arm, or if you have other upper-extremity related concerns, please consult our hand specialist Dr. Dominic Patillo for a consultation.