What is Spondylosis?
in Spinal Stenosis, SpineArticle featured on HealthPartners
As we get older, just about every part of our body will experience natural changes. And for many adults, neck and back problems are some of the not-so-fun parts of the aging process.
Spondylosis (or degenerative disc disease) is one of the most common spinal conditions adults experience. In fact, it’s estimated that around 85% of adults over the age of 60 have some degree of spondylosis.
But what is spondylosis exactly? What are the signs and symptoms of spondylosis? Is it treatable? And when should you see a doctor for any neck and back pain you might be experiencing? We answer all these questions and more.
What you should know about spondylosis
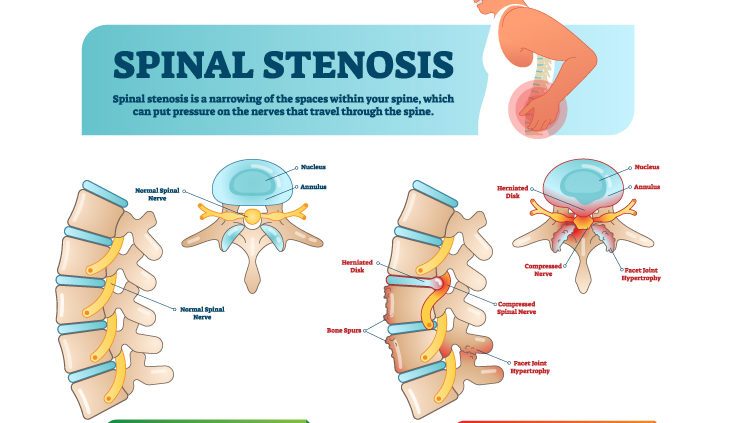
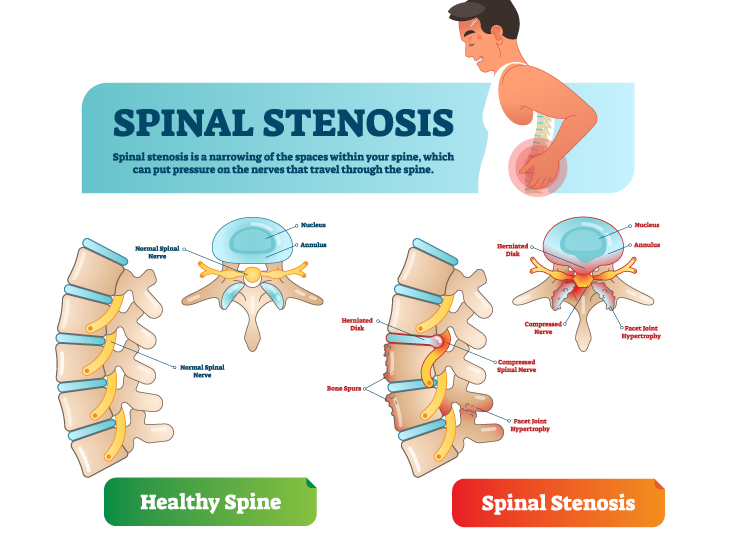
Spondylosis, or degenerative disc disease, is a form of arthritis that’s sometimes called spinal osteoarthritis. Spondylosis affects the discs in your spine, which can sometimes lead to neck pain, back pain or loss of normal spinal function.
Aging is the main cause of spondylosis
As you get older every part of your body changes, including vertebra (spinal bones) and spinal discs.
Spinal discs act as cushions between each of your neck and back’s vertebra – these discs are often described as rubbery or jelly-like. But as we age, these discs begin to dry out and thin. And that thinning places stress on every muscle, joint and ligament that holds your spine in place, which can lead to pain and decreased range of motion.
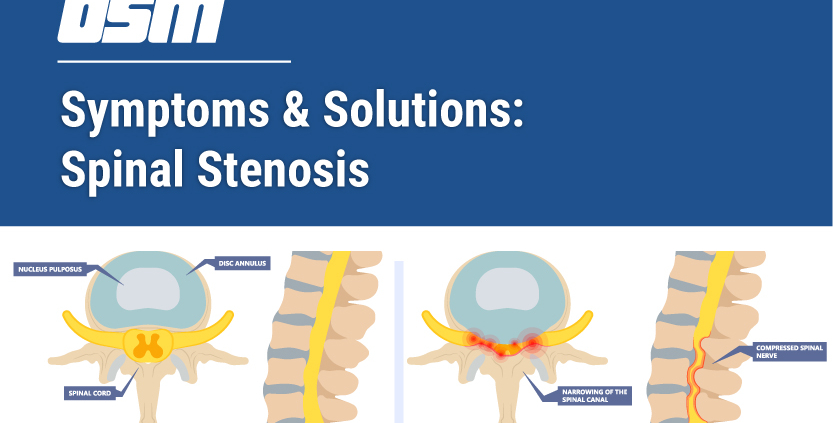
Over time, these spondylotic changes can sometimes lead to compression on one or more of the spinal nerve roots, bone spur growth or herniated discs, which may cause other symptoms.
Risk factors for spondylosis
Spondylosis is very common as you age, and you may not be able to avoid getting it. There are certain risk factors that can speed up the aging process or make you more likely to get spondylosis, including:
- Being overweight – Extra weight can put added pressure on the structures of your spine, causing them to break down faster.
- Genetic factors – People in certain families are more likely to experience spondylotic changes.
- Smoking – People who smoke are more likely to get spondylosis – and when they do, their symptoms get worse more quickly.
- A sedentary lifestyle – Sedentary behaviors are shown to increase the risk of lower back pain from spondylosis and other causes.
- Repetitive stress – Having a job that requires repetitive movement that puts stress on your spine increases your chances of developing spondylosis.
- Spinal injuries – If you’ve injured your spine in a car accident or a fall, you may be more likely to develop spondylosis.
The three types of spondylosis: Symptoms and locations
There are three different types of spondylosis. Each type is related to a specific area of your spine where the changes have occurred. These include the cervical (C), thoracic (T) and lumbar (L) regions.
Your spinal column is made up of 33 bones called vertebrae that, in part, consist of seven cervical (neck), 12 thoracic (mid back), and five lumbar (lower back) vertebrae. Between each vertebra is a disc.
The spinal column also has joints called facet joints. Their job is to connect the vertebrae and give them the flexibility to move against each other.
Spondylosis symptoms can vary from person to person. Some people may not even notice any neck or back pain or problems. While spondylosis can affect the joints anywhere along the spine, it occurs more commonly in the neck and low back.
What is cervical spondylosis?
Cervical spondylosis affects your neck, which is also called the cervical spine and represents vertebrae C1 to C7. These vertebrae connect your skull to your body and are responsible for motions like turning your head left and right, or nodding your head up and down.
Cervical spondylosis symptoms
Your neck has a big job to do. It supports the weight of your head and a wide range of movements. While many people don’t experience any symptoms of cervical spondylosis, those that do may feel:
- Neck pain, which can feel like a constant ache, get worse when you move or both (pain may also spread to your arms or shoulders)
- Neck stiffness that can get worse over time
- Muscle pain or spasms
- Headaches, especially in the back of your head
- A grinding, clicking or popping feeling when you move your neck
Is cervical spondylosis serious?
Most of the time, cervical spondylosis isn’t serious. But in some cases, cervical spondylosis can lead to the narrowing of the spinal canal, which is where the spinal cord and nerves pass through.
If the cord or nerves become compressed (or pinched), you may experience the following symptoms and should see a doctor as soon as possible:
- Numbness, tingling or shooting pain in your shoulders, arms or hands, or what can feel like an electrical sensation when you flex your neck forward
- Difficulty walking or lack of coordination
- Loss of bladder and bowel control (rare)
What is thoracic spondylosis?
Your thoracic spine, T1 through T12, picks up where your cervical spine leaves off. It continues to protect your spinal cord, and also connects to and supports your rib cage.
As the “trunk” or middle part of your back, these 12 vertebrae are stable and sturdy. As a result, thoracic spondylosis is the least common type of degenerative disc disease.
Thoracic spondylosis symptoms
Most people do not experience any symptoms. But if symptoms are present, they may include:
- Stiffness or soreness in the middle-back
- Pain in the chest and upper abdomen
- Pain radiating down the back or legs
- Weakness or tingling in the arms or legs
- Increased pain with activity
Is thoracic spondylosis serious?
Thoracic spondylosis is not usually serious, but it can worsen over time without treatment. Sometimes more serious symptoms can develop. If you experience sudden loss of motor control or walking becomes difficult, get medical care immediately.
What is lumbar spondylosis?
Lumbar spondylosis impacts your lower spine, L1 through L5. More specifically, the lumbar region is the section of the vertebrae between the thoracic spine and the sacrum. It’s the part of the spinal column that supports and distributes most of your body’s weight, making lumbar spondylosis perhaps the most common spinal osteoarthritis condition. In fact, more than 80% of those in the U.S. over the age of 40 may have lumbar spondylosis.
Lumbar spondylosis symptoms
Many people with lumbar spondylosis, don’t have any symptoms or feel pain. But some people experience symptoms such as:
- Low back pain, which can feel like constant soreness, flare up when you move, or both (back pain may also be worse in the morning and get better throughout the day)
- Back stiffness
- Weakness in the legs or feet
- Muscle pain or spasms
- Grinding, clicking or popping sensation when you sit, stand or move in a certain way
- Bladder retention (inability to urinate)
Like with cervical spondylosis, changes in spinal discs in the lumbar region can lead to nerve or cord compression. Disc herniation, which is when a disc slips or bulges through a weakened part of the spine, is also a possibility. Herniated discs are most common in the lower back and are also more common as we get older.
Is lumbar spondylosis serious?
While lumbar spondylosis usually isn’t serious, you should see a doctor right away if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Numbness, tingling or pain that radiates from your back to your buttocks, legs, feet or toes (sciatica)
- Changes in how you walk (gait) or difficulty walking
- Loss of bladder or bowel control (rare)
Spondylosis vs. spondylolysis: What’s the difference?
These two terms may look and sound almost identical, but there are key features that make the conditions different. While they can both cause back pain, spondylosis refers to the normal changes that can occur as we age. Spondylolysis is actually a stress fracture that occurs in a portion of the spine called the “pars,” and commonly caused by overuse.
How spondylosis is diagnosed
If you’re experiencing any spondylosis symptoms, you may be able to skip a trip to your primary care doctor and go straight to making an appointment with a physical therapist. Physical therapy is usually covered, but it’s always a good idea to check with your insurance provider to understand your coverage.
During your first visit, your physical therapist will likely start with a physical exam that may include:
- Asking you questions about the location and severity of any pain, stiffness or other symptoms you’re experiencing
- Evaluating your range of motion by having you move, bend or twist in different ways
- Testing for muscle weakness in your arms and legs
- Feeling along your spine to help detect any tenderness, or possible muscle spasms, bumps or areas of inflammation
In some cases, your therapist may recommend tests like X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) that allow them to take a closer look at your spine.
Treatments for spondylosis
For most people, spondylosis symptoms can be managed with at-home treatments such as over-the-counter pain relievers, hot and cold therapy, and some lifestyle modifications.
Depending on your condition, a spine specialist may also recommend pain psychology, acupuncture or injections for longer-term, yet still temporary, pain relief. And if spondylosis has led to nerve or spinal cord compression, surgery may be helpful to relieve the pressure.
But stretching and activity may be the most important step for managing pain or other spondylosis symptoms. That’s because movement is important for keeping all of your body’s muscles, ligaments and joints in working order. And working with a spine physical therapist can help.
Spine physical therapists can teach you targeted stretches and exercises to strengthen your neck and back to reduce spondylosis-related pain and stiffness. A spine strengthening program is specifically designed for people with chronic back pain.
Take the first step toward neck and back pain relief
While you can’t stop your body from aging, there are steps you can take to manage the neck and back pain that can come with it.
If you’ve recently started noticing regular neck or back pain and stiffness, and it doesn’t seem to be subsiding, a great first step can be making an appointment with a spine physical therapist.
The Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Center of Oregon is an award-winning, board-certified orthopedic group located in downtown Portland Oregon. We utilize both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, foot and ankle conditions, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors and congenital disorders.
Our mission is to return our patients back to pain-free mobility and full strength as quickly and painlessly as possible using both surgical and non-surgical orthopedic procedures.
Our expert physicians provide leading-edge, comprehensive care in the diagnosis and treatment of orthopedic conditions, including total joint replacement and sports medicine. We apply the latest state-of-the-art techniques in order to return our patients to their active lifestyle.
If you’re looking for compassionate, expert orthopedic and podiatric surgeons in Portland Oregon, contact OSM today.
Phone:
Address
1515 NW 18th Ave, 3rd Floor
Portland, OR 97209
Hours
Monday–Friday
8:00am – 4:30pm


 From
From