Bone-on-Bone Arthritis: Is Knee Replacement the Only Option?
Article featured on Orthopaedic Specialists
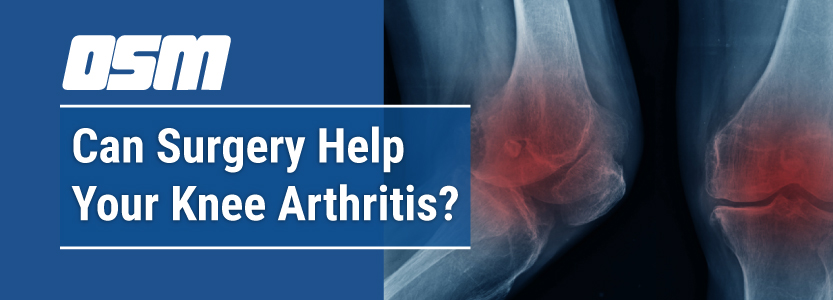
Many patients are told they have “bone-on-bone” arthritis, or end-stage osteoarthritis, on their x-ray and immediately worry that knee replacement surgery is their only option. The truth is, imaging alone should never determine whether you need surgery or not. The real indication for a knee replacement is pain that limits your daily activities. In addition, the suggestion for surgery should only come after you’ve completed a full course of conservative, non-operative treatment. If the pain is still unbearable, then imaging and discussions with your doctor can help you make the decision of whether or not to get knee replacement surgery.
Key Takeaway About a Bone-On-Bone Arthritis Diagnosis: An x-ray that shows severe arthritis does not automatically mean you need a knee replacement. Your symptoms and your response to conservative care matter far more than the image.
What Are Non-Operative Approaches to Bone-On-Bone Arthritis?
A comprehensive, non-operative approach can include treatments such as:
- Physical therapy to improve strength and mechanics
- Injection therapy such as corticosteroids or viscosupplementation to decrease inflammation
- Bracing to unload painful areas
- Activity modification to reduce stress on the joint.
Many patients experience significant improvement with these treatments, even with advanced arthritis.
What If I Still Experience Knee Pain After Non-Operative Approaches?
If, after diligently trying all these options, you are still struggling with pain, stiffness, or loss of function, then knee replacement becomes an excellent and appropriate solution. The surgery is designed to relieve pain and restore quality of life. But, it should be considered only when other methods have failed. It takes a long time to recover from knee replacement surgery and, like all surgeries, there are certain issues that can arise from it.
Allowing your body to heal itself naturally is often the best route. But, pain should never take away from your quality of life, especially with our advances in modern medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bone-On-Bone Arthritis
- What can be done for bone-on-bone arthritis? Treatment options for osteoarthritis include non-operative methods like physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, braces or other assistance devices, and lifestyle changes. Surgical treatment can include a partial knee replacement or a full knee replacement surgery.
- What stage of arthritis is bone-on-bone arthritis? There is no medical diagnosis for ‘bone-on-bone”. The term simply describes late-stage, advanced, or severe osteoarthritis. Some medical experts may also refer to it as end-stage osteoarthritis.
- Is bone-on-bone arthritis serious? End-stage arthritis is only as serious as the pain level and frequency of flare-ups. If imaging tells you that you have ‘bone-on-bone arthritis’ but you haven’t experienced any unordinary levels of pain, or your arthritic flare-ups don’t bother you often, it might not be so serious as to consider surgery.
- Can you live with untreated bone-on-bone arthritis? Yes, of course! Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis and affects a large portion of adults as they age. There are several ways to offset the symptoms and manage the condition that don’t require a doctor’s prescription or any medical intervention.
The Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Center of Oregon
The Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Center of Oregon (OSM) is an award-winning, board-certified orthopedic and sports medicine practice serving Lake Oswego, Portland, Scappoose, and surrounding Oregon communities. Our main clinic is located in Lake Oswego, with additional locations in Portland and Scappoose.
OSM provides comprehensive orthopedic care, sports medicine, spine care, joint replacement, foot and ankle surgery, hand and upper extremity care, and fracture treatment. Our physicians treat a wide range of conditions including sports injuries, arthritis, joint pain, spine conditions, ligament and tendon injuries, fractures, and degenerative musculoskeletal disorders using both surgical and nonsurgical approaches.
Our mission is to help patients return to pain-free movement, strength, and function through personalized treatment plans and advanced orthopedic techniques.
OSM Locations
Lake Oswego (Main Clinic)
17355 Lower Boones Ferry Rd, Suite 100A
Lake Oswego, OR 97035
Portland
5050 NE Hoyt St, Suite 668
Portland, OR 97213
Scappoose
51385 SW Old Portland Rd, Suite A
Scappoose, OR 97056
Phone: 503-224-8399
Hours: Mon–Thurs, 8:00am–4:30pm/ Friday 8:00am–1:00pm
If you are looking for experienced orthopedic surgeons, sports medicine specialists, spine doctors, or foot and ankle experts in Lake Oswego, Portland, or Scappoose, contact The Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Center of Oregon today.