Total Knee Replacement
If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities, such as walking or climbing stairs. You may even begin to feel pain while you are sitting or lying down.
If nonsurgical treatments like medications and using walking supports are no longer helpful, you may want to consider total knee replacement surgery. Joint replacement surgery is a safe and effective procedure to relieve pain, correct leg deformity, and help you resume normal activities.
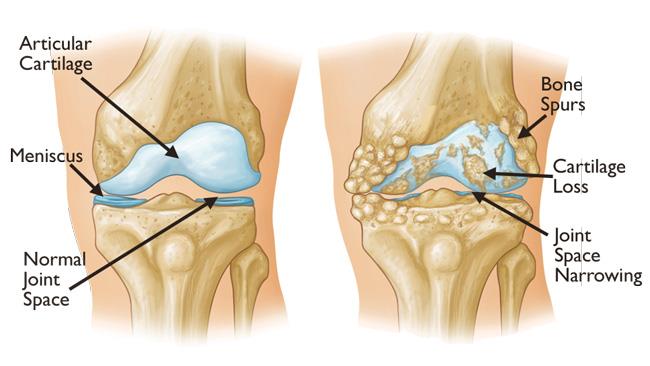
Osteoarthritis often results in bone rubbing on bone. Bone spurs are a common feature of this form of arthritis. Image courtesy of AAOS.
Common Causes of Chronic Knee Pain
The most common cause of chronic knee pain and disability is arthritis. Although there are many types of arthritis, most knee pain is caused by just three types: osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis. This is an age-related “wear and tear” type of arthritis. It usually occurs in people 50 years of age and older, but may occur in younger people, too. The cartilage that cushions the bones of the knee softens and wears away. The bones then rub against one another, causing knee pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. This is a disease in which the synovial membrane that surrounds the joint becomes inflamed and thickened. This chronic inflammation can damage the cartilage and eventually cause cartilage loss, pain, and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of a group of disorders termed “inflammatory arthritis.”
- Post-traumatic arthritis. This can follow a serious knee injury. Fractures of the bones surrounding the knee or tears of the knee ligaments may damage the articular cartilage over time, causing knee pain and limiting knee function.
Video courtesy of Visual Health Solutions, Inc.
Total Knee Replacement Surgical Procedure
A knee replacement (also called knee arthroplasty) might be more accurately termed a knee “resurfacing” because only the surface of the bones are actually replaced.
There are four basic steps to a knee replacement procedure.
- Prepare the bone. The damaged cartilage surfaces at the ends of the femur and tibia are removed along with a small amount of underlying bone.
- Position the metal implants. The removed cartilage and bone is replaced with metal components that recreate the surface of the joint. These metal parts may be cemented or “press-fit” into the bone.
- Resurface the patella. The undersurface of the patella (kneecap) is cut and resurfaced with a plastic button. Some surgeons do not resurface the patella, depending upon the case.
- Insert a spacer. A medical-grade plastic spacer is inserted between the metal components to create a smooth gliding surface.
Recovering from your surgery
After surgery, you will feel some pain. This is a natural part of the healing process. Your doctor and nurses will work to reduce your pain, which can help you recover from surgery faster.
Medications are often prescribed for short-term pain relief after surgery. Many types of medicines are available to help manage pain, including opioids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and local anesthetics. Your doctor may use a combination of these medications to improve pain relief, as well as minimize the need for opioids.
Be aware that although opioids help relieve pain after surgery, they are a narcotic and can be addictive. Opioid dependency and overdose has become a critical public health issue in the U.S. It is important to use opioids only as directed by your doctor. As soon as your pain begins to improve, stop taking opioids. Talk to your doctor if your pain has not begun to improve within a few days of your surgery.
Blood Clot Prevention
Your orthopaedic surgeon may prescribe one or more measures to prevent blood clots and decrease leg swelling. These may include special support hose, inflatable leg coverings (compression boots), and blood thinners.
Foot and ankle movement also is encouraged immediately following surgery to increase blood flow in your leg muscles to help prevent leg swelling and blood clots.
Avoiding Problems After Surgery
Follow your orthopaedic surgeon’s instructions carefully to reduce the risk of blood clots developing during the first several weeks of your recovery. He or she may recommend that you continue taking the blood thinning medication you started in the hospital. Notify your doctor immediately if you develop any of the following warning signs.
Warning signs of blood clots. The warning signs of possible blood clots in your leg include:
- Increasing pain in your calf
- Tenderness or redness above or below your knee
- New or increasing swelling in your calf, ankle, and foot
Warning signs of pulmonary embolism. The warning signs that a blood clot has traveled to your lung include:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Sudden onset of chest pain
- Localized chest pain with coughing
Preventing Infection
A common cause of infection following total knee replacement surgery is from bacteria that enter the bloodstream during dental procedures, urinary tract infections, or skin infections. These bacteria can lodge around your knee replacement and cause an infection.
After knee replacement, patients with certain risk factors may need to take antibiotics prior to dental work, including dental cleanings, or before any surgical procedure that could allow bacteria to enter the bloodstream. Your orthopaedic surgeon will discuss with you whether taking preventive antibiotics before dental procedures is needed in your situation.
Warning signs of infection. Notify your doctor immediately if you develop any of the following signs of a possible knee replacement infection:
- Persistent fever (higher than 100°F orally)
- Shaking chills
- Increasing redness, tenderness, or swelling of the knee wound
- Drainage from the knee wound
- Increasing knee pain with both activity and rest
Avoiding Falls
A fall during the first few weeks after surgery can damage your new knee and may result in a need for further surgery. Stairs are a particular hazard until your knee is strong and mobile. You should use a cane, crutches, a walker, hand rails, or have someone to help you until you have improved your balance, flexibility, and strength.
Your surgeon and physical therapist will help you decide what assistive aides will be required following surgery and when those aides can safely be discontinued.