Spine Pain: 3 Rare but Severe Conditions that Might Affect You
By Christine Rhodes, MS | Reviewed By Forest Tennant, MD, DrPH | Article Featured on Practical Pain Management
Injuries, abnormalities, and gradual wear and tear can lead to the development of severe spine pain. With straining, twisting, and spraining, soft tissues around the spine can become inflamed, causing pain and muscle spasms over time. This pain can be very debilitating and cause a patient to significantly reduce their day-to-day activities.
The severe pain that accompanies the following rare spine conditions detailed below can affect you or a loved one. Being knowledgeable about these conditions can help you to speak to your doctor if you feel you may have similar symptoms.
Sleep Hygiene and Back Pain
Article Featured on Spine Health Institute
Give Your Spine a Good Night’s Rest
Sleep. It’s one of the most natural and nurturing human activities, and it’s something we all require to keep our minds and bodies functioning properly. But did you know you can actually sleep the WRONG way? Think about the last time you awoke with a stiff neck after lying in an awkward position. Or maybe your back started hurting the second you got up for work. Whether you aggravated an old injury or created a new one, it happened when you weren’t even conscious!
The truth is, each of us can benefit by following certain “sleep strategies” that minimize the pressure on our spinal column while we’re at rest. This starts with learning the proper way to get into and out of bed so as to reduce unnecessary twisting of the spine.
Getting Into Bed
Obviously, if you’re prone to chronic back or neck pain, or if you’re trying to recover from a recent back injury, having a good mattress is a key to your comfort. While mattress shopping isn’t fun – or cheap! – it’s worth knowing what to look for when the time comes. Our Spine U library has a quick video that demonstrates how to choose the best mattress for your back.
That said, even the best mattress can’t keep you from straining a muscle when you’re getting into or out of bed. That’s why we recommend the “log roll” sequence, especially for those just recovering from a back injury. Here’s how it’s done:
- First, sit on the edge of the bed and use your arms to slowly lower your body down onto your side while bringing your legs and feet onto the bed.
- Roll onto your back while keeping your back and hips in line. Avoid twisting your back by tightening your abdominal muscles.
- To get up, slowly roll onto your side and slide your legs off the side of the bed. Be sure to keep your abdominal muscles tight.
- With your elbow and hand, push into the mattress and lift up into a sitting position.
This quick video demonstrates the log roll.
Lying on Your Back
If you typically sleep on your back, learn the correct “supine” position to avoid putting undue stress on parts of your spine.
- Start by completing the log roll sequence to lie down.
- Use a medium-sized pillow under your head to ensure that your body and head are at equal height.
- If needed, place a small pillow in the curve of your lower back for support.
- Place one or two pillows under your knees to keep your spine in a neutral position.
This video demonstrates the proper supine position.
Sleeping on Your Side
If you prefer lying on your side, it’s important to keep your hips and neck in alignment. Here’s how.
- Use the log roll sequence to get into bed.
- Place a medium-sized pillow under your head so your head and body are raised by the same amount.
- If needed, place a small towel roll in the curve of your neck.
- Place a thin- to medium-sized pillow between your knees to help support your lower back.
This video demonstrates the proper side-sleeping technique.
For Stomach Sleepers
In general, it’s not very wise to sleep on your stomach because of the strain that this position puts on your back and neck. But if this is the only way you’re able to sleep, you can reduce the pressure on your spinal column this way.
- Start the logroll sequence and use your arms to lower your body down on your stomach while lifting your legs onto the bed.
- Use a very thin pillow or no pillow under your head to keep your neck in line with your body.
- Place a thin or medium-size pillow under your stomach and pelvic region to help keep your spine in a neutral position.
- Bring one leg to your side and slightly bend it. Place a medium pillow underneath your knee to relieve pressure on your lower back.
Here’s a video that shows the best possible way to sleep on your stomach.
Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Center of Oregon is an award-winning, board-certified orthopedic group located in downtown Portland Oregon. We utilize both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors and congenital disorders.
Our mission is to return our patients back to pain-free mobility and full strength as quickly and painlessly as possible using both surgical and non-surgical orthopedic procedures.
Our expert physicians provide leading-edge, comprehensive care in the diagnosis and treatment of orthopedic conditions, including total joint replacement and sports medicine. We apply the latest state-of-the-art techniques in order to return our patients to their active lifestyle.
If you’re looking for compassionate, expert orthopedic surgeons in Portland Oregon, contact OSM today.
Phone:
503-224-8399
Address
17355 Lower Boones Ferry Rd Suite 100A
Lake Oswego, OR 97035
Hours
Monday–Friday
8:00am – 4:30pm
How to Keep Your Spine Healthy As You Age
Article Featured on Spine Health Institute
As we get older, it’s not uncommon to experience increased aches, pains and joint stiffness. Many of us assume this discomfort just goes with the territory – and in fact, when it comes to the spine, some decline in function and flexibility may be expected as the bones and intervertebral disks begin to deteriorate over time.
But there are several things you can do right now to help maintain your spine’s flexibility and comfort well into your golden years.
Here’s what you should know about what happens to your spine as you age, common spinal conditions in older adults, and ways to help prevent back pain and injuries in the future.
Back Pain: Common Spine Problems & Causes of Back Pain
Reviewed By: Tyler Wheeler, MD | Article Featured on Medicinenet.com
Are you glad you can stand or sit upright? Thank your spine, a stack of little bones called vertebrae along the center of your back, from your seat to your neck. It supports your head, shoulders, and upper body. Your spine plays another key role: The vertebrae make a tunnel for your spinal cord. That’s the set of nerves that connect your brain to most of your body.
Lumbar Spine Surgery
Article Featured on Spine Health
Lumbar surgery refers to any type of surgery in the lumbar spine, or lower back, between one or more of the L1-S1 levels. There are two general types of lumbar spine surgery that comprise the most common surgical procedures for the lower back:
Lumbar Decompression
The goal of a decompression surgery is usually to relieve pain caused by nerve root pinching. There are two common causes of lumbar nerve root pressure: from a lumbar herniated disc or lumbar spinal stenosis.
This type of pain is usually referred to as a radiculopathy, or sciatica.
A decompression surgery involves removing a small portion of the bone over the nerve root and/or disc material from under the nerve root to relieve pinching of the nerve and provide more room for the nerve to heal. The most common types of decompression surgery are microdiscectomy and laminectomy.
There are also a few alternatives available to the above two standard procedures, such as an X-STOP which is a possible option instead of a laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis.
Lumbar Fusion
The goal of a lumbar fusion is to stop the pain at a painful motion segment in the lower back. Most commonly, this type of surgery is performed for pain and disability caused by lumbar degenerative disc disease or a spondylolisthesis.
A spinal fusion surgery involves using a bone graft to stop the motion at a painful vertebral segment, which in turn should decrease pain generated from the joint. Spine surgery instrumentation (medical devices), bone graft procedures, and a bone stimulator are sometimes used along with spinal fusion.
There are also many surgical approaches to performing spinal fusion, such as ALIF, PLIF, XLIF, TLIF, posterolateral gutter fusion, anterior/posterior fusion, and certain minimally invasive approaches.
In addition to the above conditions, decompression and/or spinal fusion may be performed to address other types of lumbar spine pathologies, such as infection or tumors.
Lumbar Spine Surgery Alternatives
In addition to the traditional one-level fusion or decompression surgery that is done for lumbar degenerative disc disease or spinal stenosis, respectively, there are a number of surgical alternatives available. Several of the most common ones include:
Artificial Disc Replacement
Artificial disc technology can be used in specific cases of lumbar degenerative disc disease.
Motion Preservation Technologies
It should be known that while spinal fusion has been a classical treatment for ongoing pain and disability from the lumbar spine, alternatives to fusion do exist for posterior conditions (problems in the back of the lumbar spine) such as spinal stenosis. Inserting an interspinous process spacer, such as the X-STOP device, can actually preserve motion as opposed to stopping it via fusion.
Vertebral Augmentation
A surgery called vertebral augmentation may be done to treat pathological fractures from tumors or osteoporosis.
Multilevel Lumbar Fusion
Lumbar spine fusion surgery for symptomatic degenerative disc disease is typically done on one level of the spine (most commonly toward the bottom of the spine, at L5-S1 or L4-L5). In certain cases it may be done on two levels, and only very rarely would it be considered on 3 or more levels. Multilevel spine fusion may be indicated in cases of scoliosis.
There are only two things that surgery can do. Surgery can decompress a nerve root or it can stabilize a painful motion segment. So we have to identify a nerve root that’s pinched or we have to identify a painful motion segment. And if we can do that, that would make you a candidate for surgery. Just having pain and having failed conservative treatment is not an indication for surgery if there is no pathological cause of the pain – it doesn’t mean there’s not pain, but we have to identify the cause of pain in order to be able to correct it. The only thing surgery can do is actually correct an anatomical defect, so we have to be able to identify it.
Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Center of Oregon is an award-winning, board-certified orthopedic group located in downtown Portland Oregon. We utilize both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors and congenital disorders.
Our mission is to return our patients back to pain-free mobility and full strength as quickly and painlessly as possible using both surgical and non-surgical orthopedic procedures.
Our expert physicians provide leading-edge, comprehensive care in the diagnosis and treatment of orthopedic conditions, including total joint replacement and sports medicine. We apply the latest state-of-the-art techniques in order to return our patients to their active lifestyle.
If you’re looking for compassionate, expert orthopedic surgeons in Portland Oregon, contact OSM today.
Phone:
503-224-8399
Address
17355 Lower Boones Ferry Rd Suite 100A
Lake Oswego, OR 97035
Hours
Monday–Friday
8:00am – 4:30pm
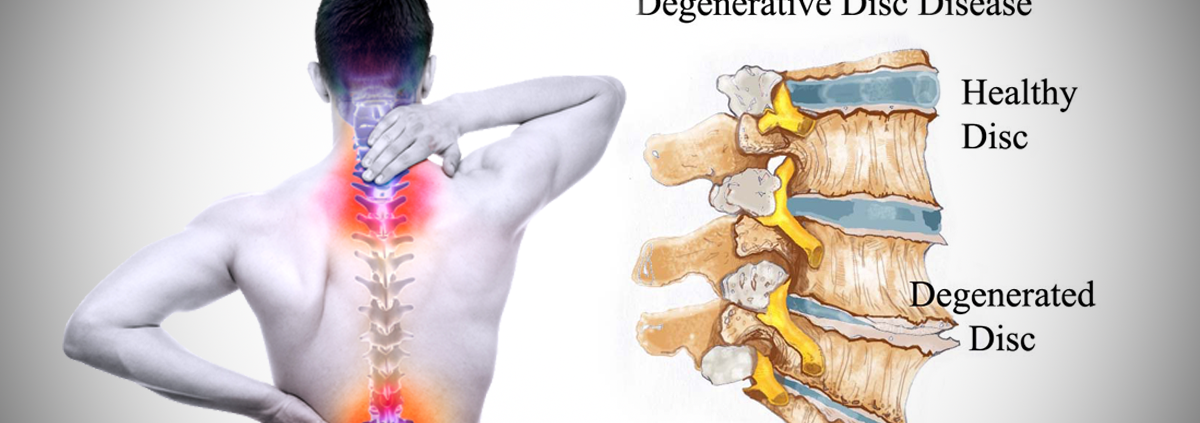
What Is Degenerative Disc Disease?
By Brian McHugh, MD | Featured on Spine Health
Degenerative disc disease is one of the most common causes of low back and neck pain, and also one of the most misunderstood.
6 Low Back Pain Symptoms, Locations, Causes & Treatments
Article Featured on eMedicineHealth
What Should I Know About Low Back Pain?
What Is the medical definition of low back pain?
Pain in the lower back or low back pain is a common concern, affecting up to 80% of Americans at some point in their lifetime. Many will have more than one episode. Low back pain is not a specific disease, rather it is a symptom that may occur from a variety of different processes. In up to 85% of people with low back pain, despite a thorough medical examination, no specific cause of the pain can be identified.
Adult Spondylolisthesis in the Low Back
Article Featured on AAOS
In spondylolisthesis, one of the bones in your spine — called a vertebra — slips forward and out of place. This may occur anywhere along the spine, but is most common in the lower back (lumbar spine). In some people, this causes no symptoms at all. Others may have back and leg pain that ranges from mild to severe.
How to tell if you have a Herniated Disk
Article Featured on AAOS
A common source of back or neck pain is a herniated disk. Sometimes called a “slipped” or “ruptured” disk, this condition most often occurs in the lower back, as well as the smaller disks in the neck.
Although a herniated disk can sometimes be very painful, most people feel much better with just a few months of simple, nonsurgical treatments.