How Obesity Impacts Your Joints
Article featured on Cary Orthopaedics
How Obesity Impacts Your Joints
When discussing health conditions caused by obesity, we most often hear about diabetes, heart disease and stroke. But did you know your weight can have a significant impact on your bones, joints and muscles, too? In this article, we address how obesity impacts your joints and ways to prevent joint damage with weight loss.
Obesity has become one of the most common diseases negatively affecting bone and joint health. More than 40 percent of adults in the United States are considered obese. In North Carolina, the percentage of obese adults is between 30% and 35%.
The percentage of adults with obesity has more than doubled over the past 30 years, and with it, so have the number of joint problems. Obesity can damage joints and cause other orthopedic health problems.
With these staggering statistics, it’s time to take a closer look at the impact of obesity on joint health.
How to define obesity
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has defined weight-to-height ratios by calculating a person’s body mass index, or BMI. A BMI that is too low is underweight, and one that exceeds healthy ranges is considered overweight or obese.
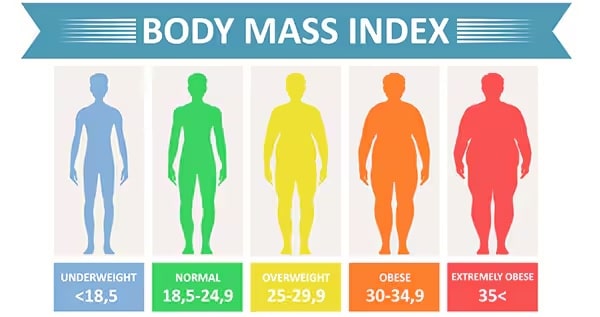
To calculate your body mass index, divide your weight by your height squared, then multiply that number by 703. Use the CDC’s BMI calculator to determine your BMI.
Being overweight causes joint damage
How does obesity affect your joints? Obesity increases your risk of joint pain and damage. It is a top risk factor for initiating and progressing osteoarthritis in load-bearing joints like the knee, hip and ankle.
The more weight placed on a joint, the more stressed the joint becomes. The smooth cartilage at the ends of the bones begins to wear down and become damaged. Osteoarthritis develops as the cartilage is worn down and pain and stiffness in the joint increase. Additional weight on the joint adds even more stress, pressure and pain.
Extra weight also puts pressure on the tendons, or connecting tissue, around the joints. Tendons connect muscles to the bones, so any extra weight pushing down on joints causes the tendons to become inflamed, leading to tendonitis.
The effects of obesity are felt especially in the hip and knee joints. Studies consistently show that obesity causes higher rates of osteoarthritis in the knees. Osteoarthritis is one of the most prevalent painful joint conditions.
Each pound of body weight is equivalent to four to six pounds of pressure on each knee joint. For example, a person who is 10 pounds overweight has an extra 40 to 60 pounds of pressure on their knees. A person who is 100 pounds overweight has an additional 400 to 600 pounds of weight on their knees.
With the number of steps most people take daily, it’s easy to see how the added pressure leads to significant damage in weight-bearing joints.
This is why obese individuals have a 20 times higher likelihood of needing a knee replacement than those within a healthy weight. The effects of obesity can also alter people’s gait and the stress placed on other joints.
Obesity causes health challenges
Being overweight puts you at risk for additional problems such as rotator cuff tendonitis, shoulder impingements, fractures in the leg or ankle, meniscal tears, plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis and other problems.
Falling can also cause problems for heavy people. Low-energy falls by obese people can result in spontaneous knee dislocations, meniscal tears and other complications. Ankle fractures happen more often and are usually worse for people who are overweight as opposed to those with a healthy weight.
Obtaining accurate diagnostic imaging for obese patients can be a challenge. Many advanced imaging machines have weight limits, requiring special appointments or preventing imaging at all.
Overweight patients with a high BMI often develop arthritis at a younger age. Needing joint replacement at a younger age complicates treatment because the replacement is more likely to wear out in the patient’s lifetime.
Additionally, orthopedic surgery on obese patients often takes longer, leading to an extended period of anesthesia.
Obese patients may have multiple complications following surgeries, including joint replacement surgery. Studies have found a higher chance of blood clots, infections, chronic pain, failure of implants and dislocation after a hip replacement.
Weight loss helps reduce joint pain
If you are diagnosed with obesity, it is essential to recognize what the excessive wear and tear can do to your body. Now that you understand how obesity impacts your joints, what can you do about it? You can make positive, healthy choices to change your health.
You can lose weight to ease the pressure on your joints. Losing just 10 pounds can decrease the progression of osteoarthritis in the knee by 50 percent. It can also reduce the force placed on the knee with every step by 30 to 60 pounds.
Losing weight has been proven to substantially decrease joint pain, reduce the likelihood of weight-related tendonitis and fractures, and lessen the risk of developing osteoarthritis in the knee.
The development of osteoarthritis is related to weakness in the quadriceps muscles in the legs of obese people. The good news is that exercises focusing on increasing muscle strength can reduce arthritis pain.
Achieve a healthy weight to help joints
Weight loss is often easier said than done. However, following a weight loss program combining nutrition and physical activity can help you reach a healthy weight.
Talk with your physician about meeting with a dietician or nutrition specialist to create an eating plan that will enable you to succeed. What you eat matters just as much as how often you exercise. Choose to feed your body healthy foods like fruits, vegetables and lean proteins.
Also, plan to be physically active for at least 30 minutes five times a week. Exercise can sometimes be difficult and painful for overweight people. The bone and joint experts at Cary Orthopaedics recommend gentle, low-impact workouts when starting a weight-loss program.
Swimming or water aerobics are also excellent exercise options for overweight people with joint pain. The water relieves pressure on the joints while also providing resistance that will strengthen your muscles.
The Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Center of Oregon is an award-winning, board-certified orthopedic group located in downtown Portland Oregon. We utilize both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, foot and ankle conditions, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors and congenital disorders.
Our mission is to return our patients back to pain-free mobility and full strength as quickly and painlessly as possible using both surgical and non-surgical orthopedic procedures.
Our expert physicians provide leading-edge, comprehensive care in the diagnosis and treatment of orthopedic conditions, including total joint replacement and sports medicine. We apply the latest state-of-the-art techniques in order to return our patients to their active lifestyle.
If you’re looking for compassionate, expert orthopedic and podiatric surgeons in Portland Oregon, contact OSM today.
Phone:
Address
17355 Lower Boones Ferry Rd Suite 100A
Lake Oswego, OR 97035
Hours
Monday–Friday
8:00am – 4:30pm










