
7 Best Hip Flexor Stretches
Article featured Verywellfit
The hip flexors are a group of…

Brief Overview of Osteoarthritis of the Hip
Article featured on UCSF Health
Osteoarthritis of the hip…

Weak Hip Flexors: Signs, Symptoms, and How to Treat Them
Article featured on MedicalNewsToday, medically reviewed by Gregory…

Hip Pain: Causes and Treatments
Article on WebMD, reviewed by Tyler Wheeler, MD on March 15,…

Exercises and Stretches for Hip Pain
From Versus Arthritis
Here are some exercises designed to…
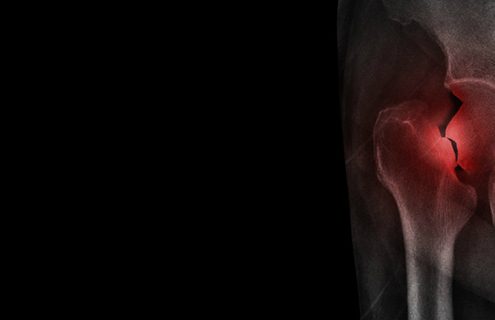
Fracture After Total Hip Replacement
Article Featured on AAOS
A periprosthetic hip fracture is…

Activities After Hip Replacement
Article Featured on AAOS
After having a hip replacement, you…
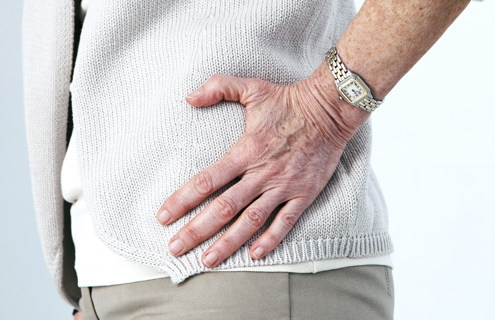
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
Article Featured on AAOS
Sometimes called "wear-and-tear"…
