What is Golfers Elbow?
Article featured on Montana Bones
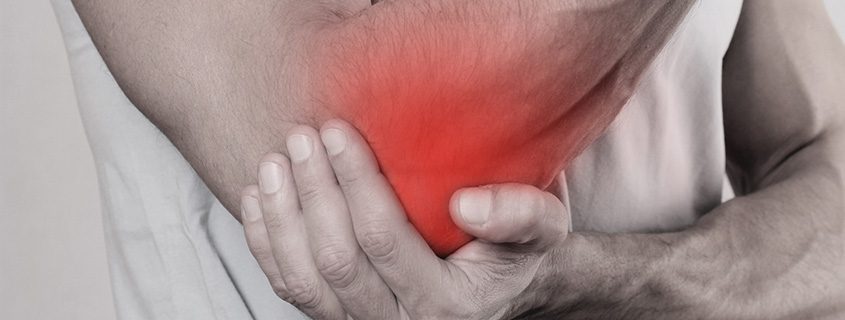
Medial epicondylitis, also known as golfer’s elbow, is a painful condition in which the tendons connecting the forearm to the elbow have become damaged due to injury or overuse. Previously thought to be a form of tendonitis, or inflammation of the tendon, medial epicondylitis is now considered to be a form of tendonosis in which the collagen fibers making up the tendon have deteriorated. Patients with this condition experience pain on the inside of the elbow that may radiate into the forearm. This pain results when the epicondyle puts pressure on the ulnar nerve, a nerve in the forearm. Most often, medial epicondylitis can be treated successfully by simple measures like resting the arm and applying ice. In some cases, however, it requires surgical correction.
While it may be caused by a single injury, medial epicondylitis is usually caused by repetitive gripping, flexing and swinging of the arm. These actions, common in golfers, cause the targeted tendons to stretch and tear. Medial epicondylitis is also frequently diagnosed in baseball pitchers, bowlers, tennis players, swimmers and individuals who do painting, raking or hammering since all of these activities involve similar arm motions. This condition is much more common in men than in women, but much less common in either than tennis elbow.The difference between the two conditions is that tennis elbow occurs on the outside of the elbow while golfer’s elbow occurs on the inside.
SYMPTOMS AND DIAGNOSIS OF MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS
Symptoms of medial epicondylitis may appear suddenly or gradually. These symptoms may include:
- Pain on the inside of the elbow or forearm
- Weakness or stiffness in the wrists and hands
- Tingling or numbness in the hand or fingers, particularly the ring finger or pinkie
The pain of medial epicondylitis may worsen with certain actions, such as swinging the arm, squeezing the hand, turning a doorknob or lifting something heavy, especially when the palm is facing downward.
DIAGNOSIS OF MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS
Medial Epicondylitis is diagnosed through physical examination, the use of X-rays and, on occasion, other diagnostic tests such as MRIs or ultrasound.
TREATMENT OF MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS
There are several simple treatment options for medial epicondylitis. The treatments for medial epicondylitis may include:
- Resting the arm
- Wearing a bandage or splint on the wrist or elbow
- Icing the affected region
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers
- Doing therapeutic exercises
- Receiving electrical stimulation treatments
- Taking prescribed corticosteroids orally or by injection
- Receiving shock wave treatments of the area
The symptoms of medial epicondylitis may resolve in weeks or may persist for months. As the pain subsides, a physical or occupational therapist may suggest different ways of moving the arm to avoid a recurrence of symptoms. If the condition lasts more than 3 to 6 months, becoming chronic, surgery may be considered.
SURGICAL REPAIR OF MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS
There are several types of surgery performed to repair medial epicondylitis. Such surgeries may be performed arthroscopically or as open surgery and are normally done outpatient with a local anesthetic. They usually take between 3 and 4 hours to complete. Most patients may return to a relatively normal routine in about 4 weeks, but may have residual discomfort, weakness or numbness for several months following surgery. Post-surgical physical therapy is usually required. Types of procedures used for surgical repair of medial epicondylitis may include:
Tendon Debridement – in which only the affected tissues within the tendon are removed, or debrided
Medial Epicondyle Release or Epicondylectomy and Ulnar Nerve Release – in which the medial epicondyle is removed, allowing the ulnar nerve to glide freely, releasing it from what is known as ulnar nerve entrapment
Ulnar Nerve Transposition – in which the forearm muscles are cut and temporarily disconnected from the epicondyle so that the ulnar nerve can be moved from behind the elbow to in front of it
RISKS OF SURGICAL REPAIR OF MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS
While the surgical procedures discussed are considered safe, there are potential risks with any surgery which may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Blood clots
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia or medications
- Post-surgical infection
- Breathing problems
Risks of the specific surgeries discussed may include a condition known as chronic regional pain syndrome, or CRPS. This complication, which is rare, may cause ongoing swelling, pain, skin discoloration and stiffness.
The Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Center of Oregon is an award-winning, board-certified orthopedic group located in downtown Portland Oregon. We utilize both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, foot and ankle conditions, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors and congenital disorders.
Our mission is to return our patients back to pain-free mobility and full strength as quickly and painlessly as possible using both surgical and non-surgical orthopedic procedures.
Our expert physicians provide leading-edge, comprehensive care in the diagnosis and treatment of orthopedic conditions, including total joint replacement and sports medicine. We apply the latest state-of-the-art techniques in order to return our patients to their active lifestyle.
If you’re looking for compassionate, expert orthopedic and podiatric surgeons in Portland Oregon, contact OSM today.
Phone:
Address
1515 NW 18th Ave, 3rd Floor
Portland, OR 97209
Hours
Monday–Friday
8:00am – 4:30pm